Eyeball
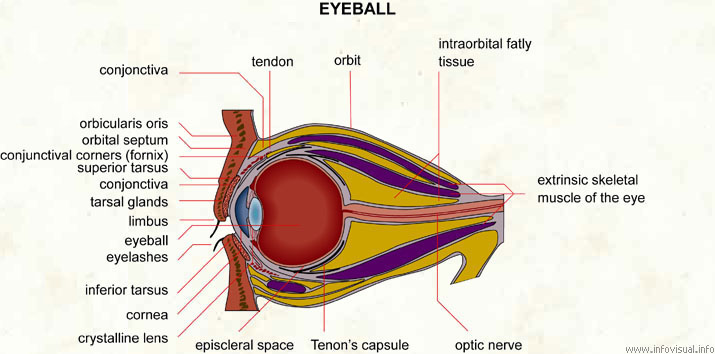
Tendon: tissue connecting the orbicular muscle of the eyelids to the bony part of the orbit.
Orbit: one of two skull cavities containing the eyeballs.
Infraorbital fatly tissue: fatty tissue on the inside of the orbit.
Extrinsic skeletal muscle of the eye: eye muscles attached to the outer wall of the eyeball.
Optic nerve: conductor of nerve impulses in the eye.
Episcleral space: interstice between the eyeball and the capsule of Tenon.
Crystalline lens: part of the eye behind the pupil that focuses light rays onto the retina.
Cornea: front part of the eye, an extension of the sclera.
Inferior tarsus: muscles that draw the lower eyelids inward.
Eyelashes: hairs along the edge of the eyelids.
Eyeball: sphere forming the eye.
Limbus: peripheral structure of an organ.
Tarsal glands: glands related to the muscles that draw the eyelids inward.
Conjunctiva: thin, translucent membrane covering the eyeball.
Superior tarsus: muscles that draw the upper eyelids inward.
Conjunctival corners (fornix): upper limit of the conjunctiva.
Orbital septum: division between the two skull cavities containing the eyes.
Orbicularis oris: muscle that closes the eyelids.
Conjunctiva: part of the conjunctiva that covers an unexposed part of the eyeball.
Photo :
EN : Eyes
FR : Œil
(pluriel les yeux)
ES : Ojo
Eyes are organs of vision that detect light. Different kinds of light-sensitive organs are found in a variety of organisms. The simplest eyes do nothing but detect whether the surroundings are light or dark. The visual fields of some such complex eyes largely overlap, to allow better depth perception, binocular vision, as in humans.