Ear
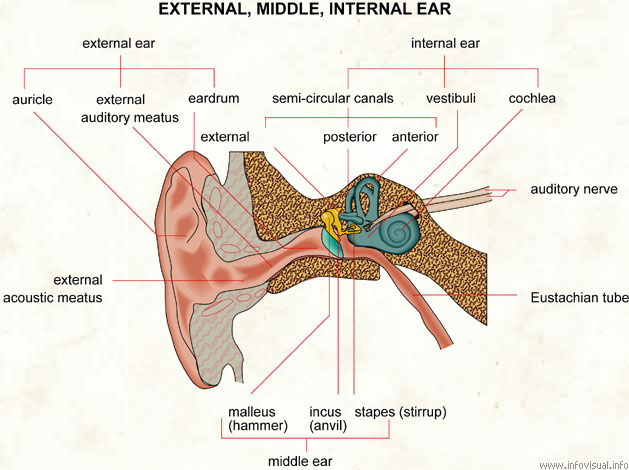
External ear: visible part of the ear.
Auricle: outer part of the external ear.
External auditory meatus: canal of the temporal bone that carries sounds to the eardrum.
Eardrum: membrane of the external ear that transmits air vibrations to the middle ear.
Internal ear: deepest part of the ear.
Semi-circular canans: crescent-shaped tubes.
External: semicircular tube closest to the external ear.
Posterior: middle semicircular tube.
Anterior: semicircular tube deepest in the ear.
Vestibuli: cavity of the internal ear.
Cochlea: part of the internal ear that converts sound vibrations to nerve impulses.
Auridory nerve: nerve related to hearing.
Eustachian tube: canal that allows equalization of air pressure on both sides of the eardrum.
Middle ear: part of the ear between the internal and external ears.
Stapes (stirrup): ossicle of the middle ear connected to the incus.
Incus (anvil): middle ossicle of the middle ear.
Malleus (hammer): first ossicle of the middle ear.
External acoustic meatus: canal of the temporal bone that carries sounds to the eardrum.
Photo :
EN : Human
ear
FR : L'oreille
humaine
ES : Oído
humano
The ear is the sense organ that detects sounds. The vertebrate ear shows a common biology from fish to humans, with variations in structure according to order and species. It not only acts as a receiver for sound, but plays a major role in the sense of balance and body position.
Animation : The Ear: the Organ of Hearing
Thanks to YouTube for allowing us to watch this video.