Arterial system
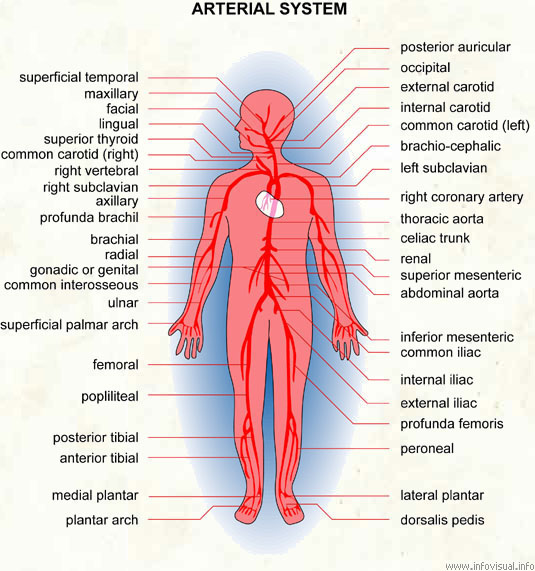
Posterior auricular: vessel carrying blood to the ear.
Occipital: vessel carrying blood to the head.
External carotid: neck vessel carrying blood to the face.
Internal carotid: neck vessel carrying blood to the brain.
Common carotid (left): vessel carrying blood to the left side of the neck.
Brachio-cephalic: main vessel of the arm.
Left subclavian: vessel carrying blood beneath the left clavicle.
Right coronary artery: vessel feeding blood to the tissues of the right side of the heart.
Thoracic aorta: main artery fo the thorax.
Celiac trunk: vessel carrying blood to the thoracic cavity.
Renal: vessel carrying blood to the kidneys.
Superior mesenteric: vessel carrying blood to the upper part of the abdomen.
Abdominal aorta: principal artery in the abdominal area.
Inferior mesenteric: vessel carrying blood to the lower part of the abdomen.
Common iliac: principal artery of the lower limb of a human being.
Internal iliac: internal branch of the iliac artery.
External iliac: external branch of the iliac artery.
Profunda femoris: vessel carrying blood towards the inside of the thigh.
Peroneal: vessel carrying blood to the lower leg.
Lateral plantar: vessel carrying blood to the side of the sole of the foot.
Dorsalis pedis: vessel carrying blood to the dorsal part fo the foot.
Plantar arch: vessel carrying blood to the instep area of the foot.
Medial plantar: vessel carrying blood to the median part of the sole of the foot.
Anterior tibial: vessel carrying blood to the front part of the lower leg.
Posterior tibial: vessel carrying blood to the back part of the lower leg.
Popliliteal: vessel carrying blood to the back of the foot.
Femoral: vessel carrying blood to the thigh.
Superficial palmar arch: vessel situated just beneath the skin of the parmal arch of the hand.
Ulnar: vessel situated in the area of the ulna.
Common interosseous: vessel situated between the two bones of the forearm.
Gonadal or genital: vessel carrying blood to the genital organs.
Radial: vessel situated in the area of the radius.
Brachial: vessel carrying blood to the arm.
Profunda brachial: vessel carrying blood towards the interior of the arm.
Axillary: vessel carrying blood to the armpit.
Right subclavian: vessel carrying blood beneath the right clavicle.
Right vertebral: vessel situated on the right carrying blood to the vertebrae.
Common carotid (right): vessel carrying blood to the right side of the neck.
Superior thyroid: vessel carrying blood to the thyroid.
Lingual: vessel carrying blood to the tongue.
Facial: vessel carrying blood to the face.
Maxillary: vessel carrying blood to the maxillae.
Superficial temporal: vessel carrying blood to the surface of the skin, in the area of the temples.
Photo :
EN : Tongue
lower surface
FR : Langue
face inférieure
ES : Lengua
cara inferior
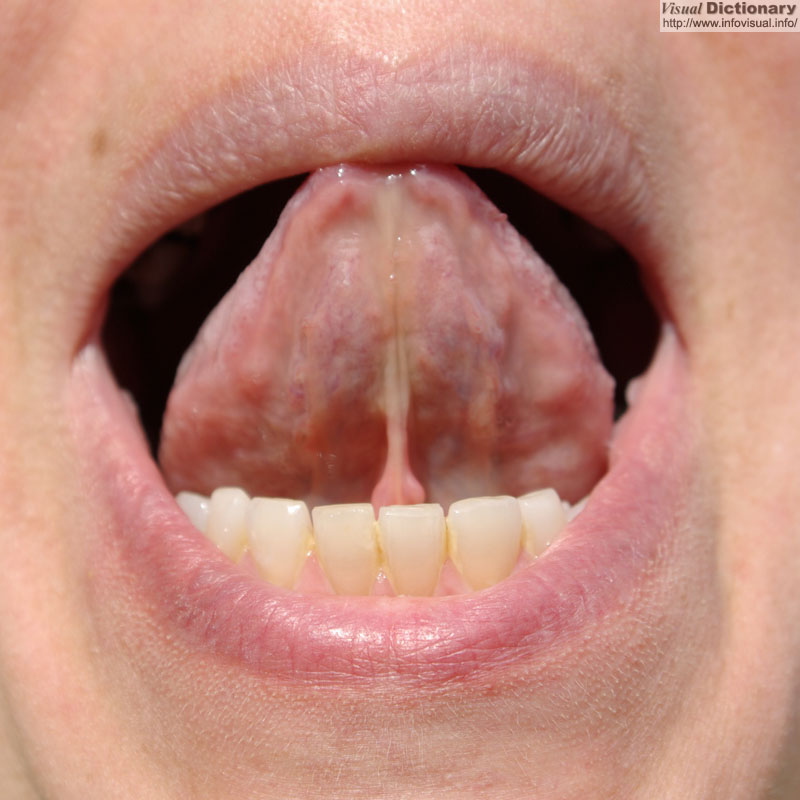
Since the tongue contains no bony supports for the muscles, the tongue is an example of a muscular hydrostat, similar in concept to an octopus arm. Instead of bony attachments, the extrinsic muscles of the tongue anchor the tongue firmly to surrounding bones and prevent the mythical possibility of 'swallowing' the tongue.
Animation : Circulatory system
Thanks to YouTube for allowing us to watch this video.