Female genital organs
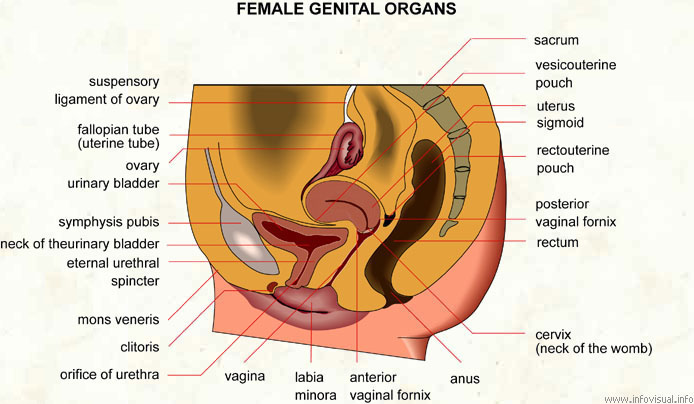
Sacrum: bone jointed with the hipbone to form the pelvis.
Vesicouterine pouch: bottom the the vesicouterine cavity.
Uterus: female genital organ that contains the fertilized egg during its development.
Sigmoid: final part of the descending colon.
Rectouterine pouch: bottom of the rectouterine cavity.
Posterior vaginal fornix: back end of the vaginal cavity.
Rectum: final part of the large intestine, between the sigmoid and the anus.
Cervix (neck of the womb): narrow part of the uterus.
Anus: end of the large intestine, through which the human body expels solid waste.
Anterior vaginal fornix: front end of the vaginal cavity.
Labia minora: one of two cutaneous folds situated within the labia majora.
Vagina: internal female genital organ, between the vulva and the uterus.
Orifice of urethra: end of the urethra.
Clitoris: erectile organ situated in the upper part of the vulva.
Mons veneris: eminence situated at the front of the female pubis, covered with hair from puberty onwards. Also called the mons pubis.
Eternal urethral sphincter: muscle used to open and close the urethra.
Neck of the urinary bladder: narrow part of the bladder.
Symphysis pubis: semi-mobile pubic joint.
Urinary bladder: pocket in which urine collects.
Ovary: one of two egg-producing genital glands.
Fallopian tube (uterine tube): conduit between the ovary and the uterus.
Suspensory ligament of ovary: tissue that holds the ovary in place.
Photo :
EN : Tongue
lower surface
FR : Langue
face inférieure
ES : Lengua
cara inferior
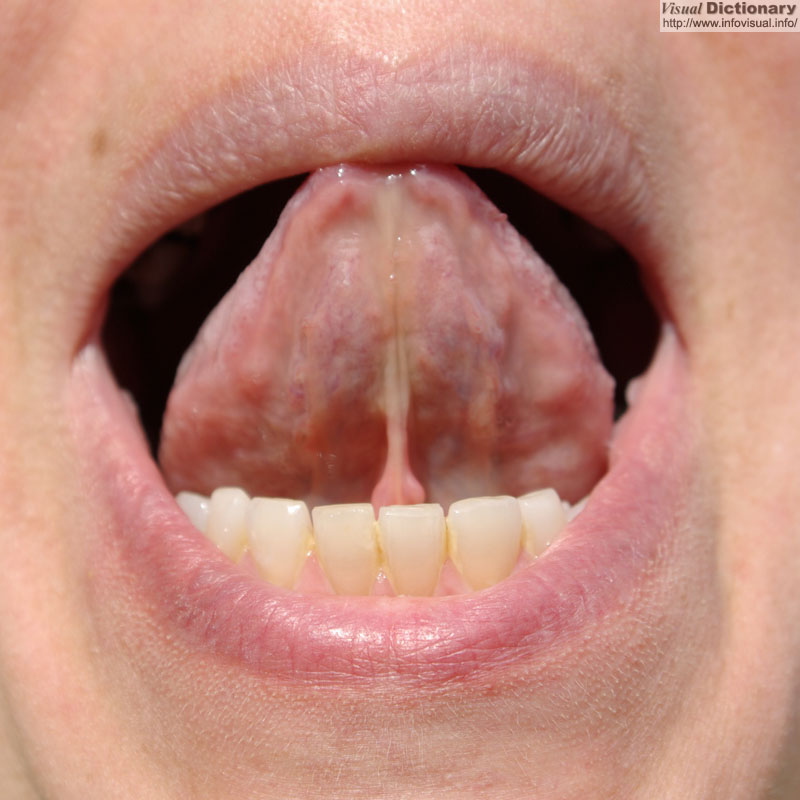
Since the tongue contains no bony supports for the muscles, the tongue is an example of a muscular hydrostat, similar in concept to an octopus arm. Instead of bony attachments, the extrinsic muscles of the tongue anchor the tongue firmly to surrounding bones and prevent the mythical possibility of 'swallowing' the tongue.