Bird
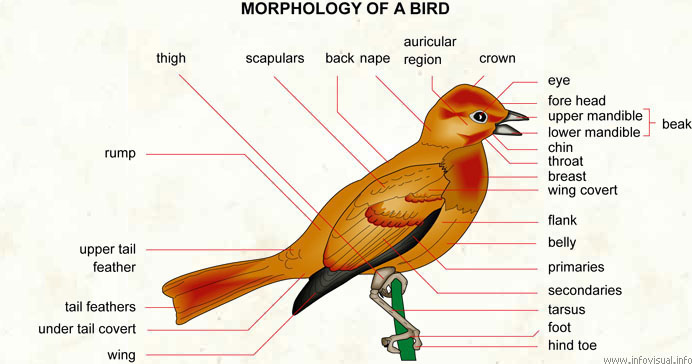
Thigh: top part of the leg of a bird.
Scapulars: shoulder feathers.
Back: back part of a bird's thorax.
Nape: back of a bird's neck.
Auricular region: part of a bird's head related to the ear.
Crown: top part of a bird's head.
Eye: sight organ of a bird.
Fore head: top part of the face.
Upper mandible: top part of the beak.
Lower mandible: lower part of the beak.
Beak: a set of upper and lower mandibles.
Chin: lower part of the face.
Throat: fron tpart of the neck.
Breast: front part of the thorax.
Wing covert: upper part of the wings.
Flank: side part of the body.
Belly: front of the abdomen.
Primaries: the largest feathers on the edge of a bird's wing.
Secondaries: large feathers between the primaries and the tertials of a bird's wing.
Tarsus: part of the leg of a bird below the thigh.
Foot: the end part of a bird's leg.
Hind toe: jointed rear appendage.
Wing: appendage of aerial locomotio.
Under tail covert: feathers under a bird's tail.
Tail feathers: feathers forming the tail of a bird.
Upper tail feather: feathers above the tail.
Rump: projection of the lower back.
Photo :
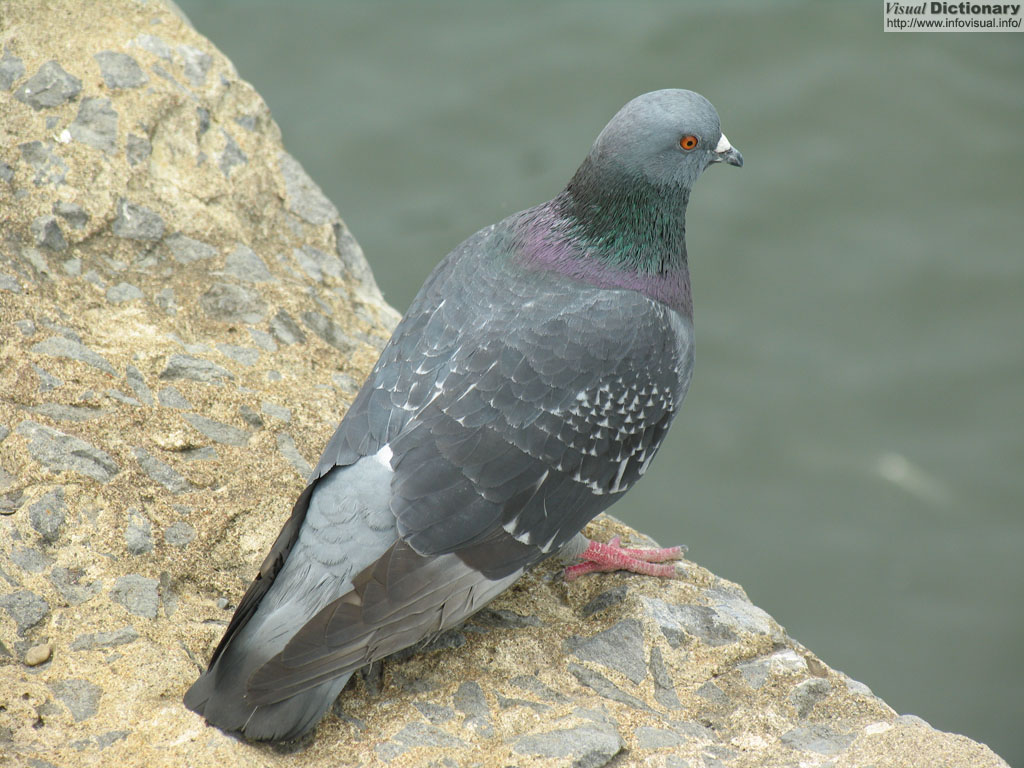

Pigeons and doves constitute the family Columbidae within the order Columbiformes, which include some 300 species of near passerine birds. In general parlance the terms "dove" and "pigeon" are used somewhat interchangeably. In ornithological practice, there is a tendency for "dove" to be used for smaller species and "pigeon" for larger ones, but this is in no way consistently applied, and historically the common names for these birds involve a great deal of variation between the term "dove" and "pigeon." This family occurs worldwide, but the greatest variety is in the Indomalaya and Australasia ecozones. The young doves and pigeons are called "squabs.". Pigeons and doves are stout-bodied birds with short necks and short slender bills with a fleshy cere.
The species commonly referred to just as the "pigeon" is the feral Rock Pigeon, common in many cities. Doves and pigeons build relatively flimsy nests from sticks and other debris, which may be placed in trees, on ledges, or on the ground, depending on species. They lay one or two eggs, and both parents care for the young, which leave the nest after 7 to 28 days. Doves feed on seeds, fruit and plants. Unlike most other birds (but see flamingo), the doves and pigeons produce "crop milk," which is secreted by a sloughing of fluid-filled cells from the lining of the crop.
Animation : Pigeon
Thanks to YouTube for allowing us to watch this video.
Objet virtuel : Pigeon
Thanks to YouTube for allowing us to watch this video.